Results of system implementationERP BAANat industrial enterprises in Russia and CIS countries
CEO
"ALFA-INTEGRATOR" - "BAAN Eurasia"
This article continues the series of articles on the implementation of ERP-class systems at Russian enterprises and enterprises in the CIS countries as the core of information support technologies for the product life cycle (IPI technologies). Based on the results of the implementation of the BaanERP system of the company "ALFA-INTEGRATOR" - "BAAN Eurasia", data is provided on the economic and production effect that the enterprise achieved when implementing the specified system.
During the period of its presence in the information technology market in Russia and the CIS countries, Alfa-Integrator Group of Companies - Baan Eurasia has implemented projects to implement the BaanERP system at many defense industry and mechanical engineering enterprises, some of them are shown in the table:
Company name | Industries |
"Hydrosila" | Mechanical engineering |
"Baltic Plant" | Shipbuilding |
"Almetyevsk Pump Plant" | Mechanical engineering |
"Ufa engine-building software" | Mechanical engineering |
NPK Irkut | Aircraft industry |
"Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aviation Production Association" | Aircraft industry |
"UralAZ" | Automotive industry |
Automotive industry |
|
Automotive industry |
|
Private Research and Production Enterprise "Elara" | Instrumentation |
"Krasnoyarsk Combine Harvester Plant" | Agricultural engineering |
Radio plant "Polyot" | Instrumentation |
Representatives of these enterprises note a significant advantage of these solutions compared to other options for ERP systems, and first of all, in terms of production. As a result of the implementation of these projects, an industry solution was created for enterprises in the mechanical engineering industry. Through the use of industry reference models and testing of the system at the largest global and domestic enterprises in the engineering industry, the cost and time of system implementation are reduced.
In 2003, the list of clients of Alfa-Integrator Group of Companies - Baan Eurasia was replenished with new enterprises: mining and chemical plant", them. Degtyarev" etc. The choice of these enterprises is due to the fact that the Russian version of the BaanERP system, localized by Alfa Integrator Group of Companies - Baan Eurasia, works effectively at enterprises in the mechanical engineering industry, offering them easily adaptable solutions.
The implementation of ERP systems can actually reduce enterprise costs, but only if these systems and solutions are used to solve problems of planning and production management at the enterprise.
The main source of reducing production costs of an enterprise from the implementation of ERP systems is a radical reduction in inventories in warehouses and in work in progress, a reduction in production cycles, because it was not for nothing that the thesis “inventories are costs” was proclaimed in Japan back in the early 70s. And this can be achieved only by transferring the enterprise through the implementation of an ERP system to modern methods of planning and production management, primarily to custom production.
Unfortunately, in Russia we have very few examples where an ERP system works to perform production management tasks. Basically, all implementation projects are focused on financial and inventory management tasks, calling it “implementation” or “productive installation” of an ERP system. And then consumers are rightly perplexed as to why there is no visible cost reduction from the implementation of an ERP system.
In cases where an enterprise uses an ERP system to plan and manage production, there is a significant reduction in inventory levels and associated working capital requirements.
To date, a number of leading enterprises in Russia and the CIS countries that have implemented BaanERP have achieved significant success both in terms of managing enterprise resources at individual stages of production, and as part of improving the activities of the entire enterprise. Below are the results of the implementation and operation of the BaanERP system at leading enterprises in Russia and the CIS countries. The achieved results show that the BaanERP system is an ideal solution in the field of resource management for both large engineering enterprises () and medium-sized ones ().
Ural plant
Number of employees :person
Industry: Automotive industry.
Main products : all-wheel drive vehicles "Ural".
About the company : The Ural Automobile Plant was founded in 2001 as a result of the restructuring of the UralAZ production complex and is the successor of its history and traditions. The new enterprise became part of the Russian holding company RusPromAvto.
Currently, the Ural Automobile Plant occupies a leading position among manufacturers of all-wheel drive trucks with the wheel arrangement 4x4, 6x6, 8x8.
Company website: www. *****
Number of users: about 1200 users. The plant has created a qualified implementation group and three support groups involved in supporting and developing the functionality of the system. Work is underway to create a Competence Center - a structure that unites BaanERP users and guarantees high-quality operation and further development of the system after implementation.
Implemented blocks:
§ Financial and economic block;
§ Sales, supply, warehouses;
§ Planning of main production;
§ The work of the procurement directorate, warehouse accounting of purchased materials and components are fully automated;
§ Personnel Management;
At the moment, the work of accounting (general ledger), settlements with suppliers and customers, fixed asset accounting, cash accounting, and financial planning are automated.
During implementation BaanERP at UralAZ, the following results were achieved:
§ Logistics operations in commercial operation are automatically reflected in accounting data, ensuring the reliability and transparency of accounting.
§ During the implementation process, many business processes of planning and accounting at the plant were revised, a transition was made from the generation of monthly reporting to operational registration and use of information. The mechanism for integrating logistics with the financial module eliminates double input of information and discrepancies in accounting and management accounting data.
§ As obvious advantages from the implementation of the system that have already been received by the plant, the following should be highlighted: a single repository of regulatory and reference information (all plant services and calculations use the same data), a reduction in the number of accounting departments, a reduction in the time frame for preparing and submitting financial statements, the availability of prompt, reliable data on material inventories in warehouses in physical and monetary terms.
§ The following indicators were achieved in 2004:
Reduction of inventories of inventory items (materials and materials) – 65,000 thousand rubles.
Reduction of property tax – 2,500 thousand rubles.
§ Cost accounting and budgeting;
§ Technical preparation of production;
§ Financial management, tax accounting;
§ Accounting.
During implementation BaanERP, the following results were achieved:
§ In production: accounting for the execution of intra-shop operations and inter-shop movements has been established, which makes it possible to control the state of work in progress (WIP), data on completed operations is transferred to the payroll subsystem, accounting and automatic pricing of defects are carried out, shift-daily assignments are generated for sections.
§ There has been a reduction in work in progress (current – about 1.4 billion rubles) due to the optimal calculation of batch sizes, compliance with the condition of matching the launch batch with the production batch, planning the launch always according to demand, clarifying the assessment of work in progress - operational (now approximately half the cost of passing the part is taken workshop).
Type of product production - “production to order”, “production to warehouse”, “batch, small-scale and single production”.
Company website: www. *****
Number of users in the system: about 1000 users.
Implemented blocks: The implementation of the localized Russian version of the management and planning system BaanERP by Alfa-Integrator Group - Baan Eurasia was carried out in the following areas:
§ Maintaining the regulatory framework. The planning basis has been formed - the regulatory framework for products
Total number of purchased products (66,000);
Total number of manufactured products (50500);
Product Specifications (45207);
Technological routes for manufacturing products (33678).
§ Manufacturing control. Production orders are processed according to the nomenclature of all products of the main production workshops, the following is carried out:
Formation and management of production orders (planning and dispatch department (PDO), workshops and companies of the main production);
Documentation of orders;
Issue of components and materials to order;
Collection of actual material costs;
Report on the operations of the technological route for manufacturing products;
Generating summary reports on the launch and release of products.
§ Planning. Planning the production of products based on the main production schedule (formation of production orders, orders for the purchase of materials and components):
The number of commercial products planned in the system – % of all products of the production budget);
The total number of production orders for which planning is carried out reaches;
The number of production orders per month delivered to workshops and companies is up to 5000;
The depth of product planning reaches 16 levels;
§ Inventory Management. Inventories of materials and components are managed to ensure production through purchase orders - the average number of orders processed per month is up to 4000.
§ Sales management. Sales management was organized through the formation of contracts and sales orders, shipment of commercial products from the enterprise's warehouses, generation of statistical data on sales in the context of the product range and areas of activity of the enterprise's marketing services.
§ Financial management. Obtaining and analyzing the financial results of the enterprise through integration with sales, supply, and production modules.
During implementation BaanERP at ChNPP "Elara", the following results were achieved:
§ Accelerating the launch of new products
§ Timely execution of orders
§ By increasing the reliability of accounting and planning with an increase in production volumes, there was a decrease in inventories of goods and materials for main production in warehouses. The balance decreased in 2002 from 140 million rubles. up to 100 million rubles, and currently decreased to 80 million rubles.
§ According to the financial department, the use of the BaanERP system to calculate the volume of purchases made it possible to reduce the volume of financing by almost 2 times with a significant increase in the volume of commercial products.
§ The Russian version of the BaanERP system, by order of the plant, was introduced into the rank of the corporate resource management system of the enterprise.
Further development of the project:
§ Management Accounting. Development of management accounting methods at the enterprise (budgeting, controlling);
§ CRM. Acquisition and implementation of the Baan – CRM “Marketing and Sales” module;
§ Barcoding. Introduction of an automatic identification system (bar coding) in the production of printed circuit boards;
§ Auxiliary production. Extension of BaanERP technologies to the production preparation system (tool production);
§ Management of geographically distributed objects. Inclusion of regional divisions of the joint-stock company (Kanash branch, Moscow representative office) into a unified management system.
(Ukraine)
Number of employees : 2,800 people
Industry: Mechanical engineering.
Main products: hydraulic units for hydraulic systems of tractors, cars, agricultural and road machines.
About the company: A leading enterprise in the CIS with a closed production cycle, including all stages of product manufacturing, from foundry to assembly and testing of finished products. The plant is a developer of its own products. The company supplies its products to the largest enterprises in Russia and abroad.
Company website: www.
Number of users: more than 200 users.
Implemented blocks: The implementation of the localized Russian version of the management and planning system BaanERP by Alfa-Integrator Group - Baan Eurasia was carried out in the following areas:
§ technical support of production,
§ planning of sales, production, inventories and purchases,
§ sales management,
§ procurement management,
§ accounting of production costs,
§ material flow management,
§ foundry management,
§ the implementation of the “Service” subsystem for planning, accounting and management of scheduled preventive maintenance of equipment and the “Finance” subsystem has begun.
During implementation BaanERP on, the following results were achieved:
§ Production regulatory and reference information has been verified, which is very important for the reliability of accounting, support of the quality management system, for the planning base, and cost accounting;
§ The structure of production management was optimized in order to increase the level of controllability and optimize the number and warehouse facilities of workshops (a large number of intermediate storerooms were eliminated);
§ A complete, reliable system for recording inventories in real time has been created, eliminating losses from theft;
§ Logistics flows for the movement of inventory items have been optimized;
§ A system for optimal planning of enterprise resources has been created (capacity and labor resources, purchases of materials and semi-finished products, work in progress and warehouse inventories);
§ The activities of all divisions of the enterprise involved in the process of production and sales of products are balanced, their activities are directed in one direction to achieve a common result;
§ Enterprise managers received real-time access to unified reliable information for making management decisions;
§ Reduced balances in production warehouses by 29.3% and the level of work in progress by 26%;
§ The level of customer service has been significantly increased due to clear planning of order execution deadlines.
Further development of the project:
§ implementation of the “Baan-Controlling” block;
§ full-scale implementation of CAD at the enterprise, integration of CAD and BaanERP systems through the PDM (PLM) system;
§ implementation of the “Baan-Project” block for planning, accounting and management of the production of non-standard equipment and design work;
§ implementation of the “Baan-Quality” block;
§ implementation of an e-commerce system with distributors, the Baan CRM system (customer relationship management).
The main conclusions that were drawn by enterprises after implementing BaanERP and obtaining the results listed above are as follows:
1. The use of an ERP-class management information system (MIS) at enterprises seeking to expand their business and increase production profitability is an objective necessity.
2. The costs of acquiring, implementing, and maintaining an IMS must be considered as investment projects. There are mechanisms for optimizing direct costs, as well as reducing the risks of owning an MIS.
3. The success of implementation and minimization of risks, with all factors being equal (sufficient funding, the will of the “first” person to achieve set goals, the right implementation strategy, etc.) depends on the presence of an implementation team and practical experience on the part of consulting structures.
4. What is needed is not consulting on implementation, but well-developed decisions on the reorganization of business processes of a particular enterprise using the functionality of the ERP systems used.
5. Reduce costs, minimize risks and increase the efficiency of using the MIS - a goal achieved by improving the production management system, which should be directly related to quantitative indicators measured and controlled by the MIS.
Expertise system for the implementation of ERP at machine-building enterprises Tikhonov A. N. Director of the State Research Institute of Information Technologies and Telecommunications State Research Institute ITT "Informika" Slide No. 1
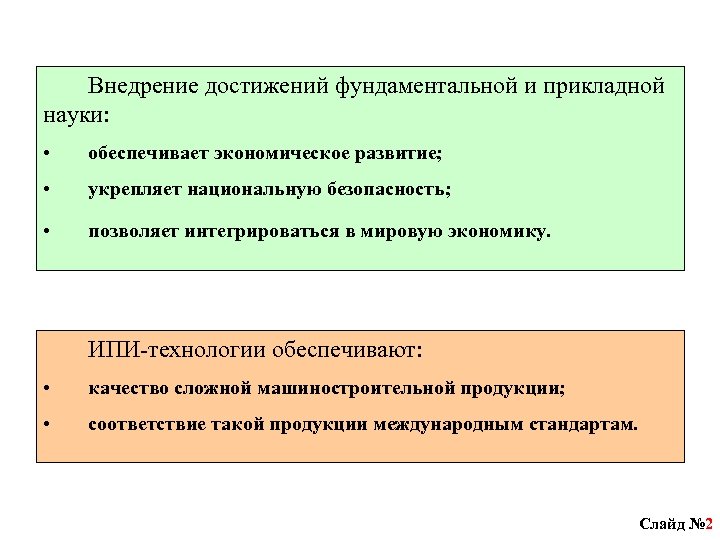 Introduction of achievements of fundamental and applied science: ensures economic development; strengthens national security; allows integration into the global economy. IPI technologies ensure: the quality of complex engineering products; compliance of such products with international standards. Slide number 2
Introduction of achievements of fundamental and applied science: ensures economic development; strengthens national security; allows integration into the global economy. IPI technologies ensure: the quality of complex engineering products; compliance of such products with international standards. Slide number 2
 Introduction of FDI technologies in US industry: direct reduction in design costs - from 10 to 30%; reduction in product development time by 1.5-2 times; reduction in time to bring new products to market – from 25 to 75%; reduction in the percentage of defects and the volume of design changes - from 23 to 73%; reduction in costs for preparing technical documentation – up to 40%; reduction in costs for the development of operational documentation – up to 30%. According to foreign sources, losses from imperfect information interaction with suppliers in the US automotive industry alone are estimated at about $1 billion per year. Slide number 3
Introduction of FDI technologies in US industry: direct reduction in design costs - from 10 to 30%; reduction in product development time by 1.5-2 times; reduction in time to bring new products to market – from 25 to 75%; reduction in the percentage of defects and the volume of design changes - from 23 to 73%; reduction in costs for preparing technical documentation – up to 40%; reduction in costs for the development of operational documentation – up to 30%. According to foreign sources, losses from imperfect information interaction with suppliers in the US automotive industry alone are estimated at about $1 billion per year. Slide number 3
 To implement IPI technologies, a line of software products is required that accompanies the product through all stages of the life cycle: Scientific research Design work Technological preparation of production Production Operation Operation Disposal Slide No. 4
To implement IPI technologies, a line of software products is required that accompanies the product through all stages of the life cycle: Scientific research Design work Technological preparation of production Production Operation Operation Disposal Slide No. 4
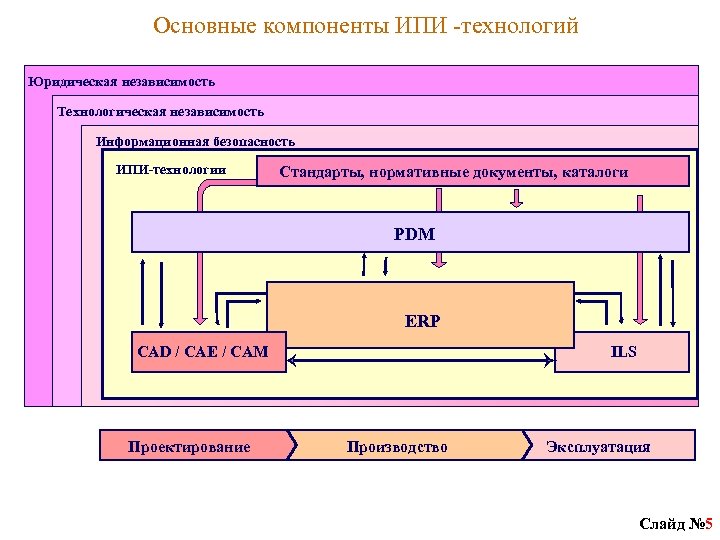 Main components of IPI technologies Legal independence Technological independence Information security IPI technologies Standards, regulations, catalogs PDM ERP CAD / CAE / CAM ILS design Production Operation Slide No. 5
Main components of IPI technologies Legal independence Technological independence Information security IPI technologies Standards, regulations, catalogs PDM ERP CAD / CAE / CAM ILS design Production Operation Slide No. 5
 Difficulties in implementing ERP systems in Russia (%) The main reason for the failure of implementing ERP systems in Russia is that enterprise managers do not participate in the project, as a result the project is delayed, becomes more expensive and ultimately remains unclaimed. Slide number 6
Difficulties in implementing ERP systems in Russia (%) The main reason for the failure of implementing ERP systems in Russia is that enterprise managers do not participate in the project, as a result the project is delayed, becomes more expensive and ultimately remains unclaimed. Slide number 6
 Ways to promote ERP systems in enterprises: through their own departments of automated control systems, IT, etc., which are interested in increasing their own influence in the enterprise by justifying their existence; this leads to increased cost and complexity of the enterprise’s technological infrastructure; through sellers of ERP systems, who contact enterprise managers in any way for the sole purpose of selling and making a profit, without caring whether the enterprise needs it or not; on the recommendation of independent consultants; the advantage of this method is the ability to avoid a rash acquisition of a system by analyzing the problem and the current situation at a given enterprise; consultants offer options; the final decision must be made by company managers. Slide number 7
Ways to promote ERP systems in enterprises: through their own departments of automated control systems, IT, etc., which are interested in increasing their own influence in the enterprise by justifying their existence; this leads to increased cost and complexity of the enterprise’s technological infrastructure; through sellers of ERP systems, who contact enterprise managers in any way for the sole purpose of selling and making a profit, without caring whether the enterprise needs it or not; on the recommendation of independent consultants; the advantage of this method is the ability to avoid a rash acquisition of a system by analyzing the problem and the current situation at a given enterprise; consultants offer options; the final decision must be made by company managers. Slide number 7
 GNII ITT "Informika" has: a scientifically based methodology for analyzing and selecting IPI technologies; a database of independent experts in the field; experience in solving similar problems in a number of international projects and federal target programs on assignments from the Ministry of Industry and Science of Russia and the Ministry of Education of Russia; as an example - examination of compliance with the Russian version of the Baan ERP system. ERP requirements for creating a basic system on its basis for defense industry enterprises in comparison with competing solutions. Slide number 8
GNII ITT "Informika" has: a scientifically based methodology for analyzing and selecting IPI technologies; a database of independent experts in the field; experience in solving similar problems in a number of international projects and federal target programs on assignments from the Ministry of Industry and Science of Russia and the Ministry of Education of Russia; as an example - examination of compliance with the Russian version of the Baan ERP system. ERP requirements for creating a basic system on its basis for defense industry enterprises in comparison with competing solutions. Slide number 8
 Expertise in the selection of a basic ERP system for defense industry enterprises. The following are taken into account: the specifics of the implementation objects; their importance for ensuring the economic and military security of the state. Software products reviewed: Baan; R 3 SAP; Oracle e. Business Suite; Galaxy; a number of other ERP systems. Slide number 9
Expertise in the selection of a basic ERP system for defense industry enterprises. The following are taken into account: the specifics of the implementation objects; their importance for ensuring the economic and military security of the state. Software products reviewed: Baan; R 3 SAP; Oracle e. Business Suite; Galaxy; a number of other ERP systems. Slide number 9
 Key requirements of the defense industry: compliance with the peculiarities of the production process at defense industry enterprises; compliance with international standards MRPII/ERP systems; implementation of the most effective methods of managing defense industry enterprises; functional requirements of a general nature (for managing production activities and the enterprise as a whole); functional requirements that take into account the specifics of defense industry enterprises; requirements for functionality from the information support side; quality requirements (compliance with ISO quality standards – 9000 version 2000; system testing; support for cross-version compatibility); means of implementation, adaptation and expansion of functionality; technological and system requirements; requirements for localization and support in accordance with operational requirements at defense industry enterprises. Slide number 10
Key requirements of the defense industry: compliance with the peculiarities of the production process at defense industry enterprises; compliance with international standards MRPII/ERP systems; implementation of the most effective methods of managing defense industry enterprises; functional requirements of a general nature (for managing production activities and the enterprise as a whole); functional requirements that take into account the specifics of defense industry enterprises; requirements for functionality from the information support side; quality requirements (compliance with ISO quality standards – 9000 version 2000; system testing; support for cross-version compatibility); means of implementation, adaptation and expansion of functionality; technological and system requirements; requirements for localization and support in accordance with operational requirements at defense industry enterprises. Slide number 10
 Properties of defense industry products: complex high-tech products, units, services and documentation; long life cycles; unique configuration of finished product copies; a large number of components and levels of input; a large range of purchased products and materials; a large flow of design and technological changes. Slide number 11
Properties of defense industry products: complex high-tech products, units, services and documentation; long life cycles; unique configuration of finished product copies; a large number of components and levels of input; a large range of purchased products and materials; a large flow of design and technological changes. Slide number 11
 Features of the production of defense industry products: development and/or production to order; combination of single and serial types; variety of forms and organization of production; diversity; long production cycles; large share of technical preparation of production; variety of technological processes - procurement, welding, foundry, machining, assembly. Slide number 12
Features of the production of defense industry products: development and/or production to order; combination of single and serial types; variety of forms and organization of production; diversity; long production cycles; large share of technical preparation of production; variety of technological processes - procurement, welding, foundry, machining, assembly. Slide number 12
 Features of the defense industry management process: diversity; combination of approaches; program-target and linear-functional multi-level (strategic, current, operational); end-to-end nature (suppliers, manufacturers, customers); multiplicity of areas of planning, accounting and planning accounting units (contracts, projects, products, kits, batches, works, operations, etc.); a wide range of organization methods and management methods; such specific techniques as advance groups, serial counting, completeness; specifics of planning and cost accounting. Slide number 13
Features of the defense industry management process: diversity; combination of approaches; program-target and linear-functional multi-level (strategic, current, operational); end-to-end nature (suppliers, manufacturers, customers); multiplicity of areas of planning, accounting and planning accounting units (contracts, projects, products, kits, batches, works, operations, etc.); a wide range of organization methods and management methods; such specific techniques as advance groups, serial counting, completeness; specifics of planning and cost accounting. Slide number 13
 Difficulties in comparative analysis: differences in understanding of ERP system standards in Russia and abroad; differences in the functional structure of ERP systems among different development companies; detection of significant differences between systems only at deep levels of their structures; differences in the structure and list of reasonable and sufficient functionality, from the point of view of development companies; dynamic ideas about evaluation criteria and properties of systems. Slide number 14
Difficulties in comparative analysis: differences in understanding of ERP system standards in Russia and abroad; differences in the functional structure of ERP systems among different development companies; detection of significant differences between systems only at deep levels of their structures; differences in the structure and list of reasonable and sufficient functionality, from the point of view of development companies; dynamic ideas about evaluation criteria and properties of systems. Slide number 14
 Necessary requirements for the basic ERP system BAAN Oracle e. Business Suite R 3 Galaktika Availability of source codes of the system from a Russian company + - - + Adaptation of the system to current legislation by a Russian company* + - - + Support and maintenance of the system by a Russian company* + - - + Russian ownership of the Russian version of the system + - - + * The founders of the company are only Russian individuals and legal entities Slide No. 15
Necessary requirements for the basic ERP system BAAN Oracle e. Business Suite R 3 Galaktika Availability of source codes of the system from a Russian company + - - + Adaptation of the system to current legislation by a Russian company* + - - + Support and maintenance of the system by a Russian company* + - - + Russian ownership of the Russian version of the system + - - + * The founders of the company are only Russian individuals and legal entities Slide No. 15
 Sufficient requirements for a basic Oracle ERP system e. Business Suite R 3 Galaktika Compliance with international standards MRPII/ERP systems + + + - Implementation of the most effective methods of managing defense industry enterprises + + + - Functionality that takes into account the specifics of defense industry enterprises + partially - 3-level architecture 2-level Customer service via the Internet + + + – Web client + + + – Oracle, Informix, Oracle Manufacturability and architecture of the BAAN system Supported databases Slide No. 16
Sufficient requirements for a basic Oracle ERP system e. Business Suite R 3 Galaktika Compliance with international standards MRPII/ERP systems + + + - Implementation of the most effective methods of managing defense industry enterprises + + + - Functionality that takes into account the specifics of defense industry enterprises + partially - 3-level architecture 2-level Customer service via the Internet + + + – Web client + + + – Oracle, Informix, Oracle Manufacturability and architecture of the BAAN system Supported databases Slide No. 16
 Quality characteristics of ERP systems Difficulties in obtaining objective information about systems, easily explained by competition in the software market Baan Oracle e. Business Suite R 3 Galaktika + + + - Duration of the company's presence on the ERP systems market 25 years 10 years Duration of product presence on the Russian market 9 years 7 years 13 years 10 years More than 16,000 About 10,000 More than 25,000 - More than 50 About 10 More than 100 About 50,002 Availability of implementations at leading enterprises of the Russian defense industry + - - No data Availability of a partner network + + 12 -24 months. 24 -36 months 36 -48 months 9 -24 months Compliance with ISO 9000 standards Total number of implementations in the world Number of implementations in Russia Average duration Slide No. 17
Quality characteristics of ERP systems Difficulties in obtaining objective information about systems, easily explained by competition in the software market Baan Oracle e. Business Suite R 3 Galaktika + + + - Duration of the company's presence on the ERP systems market 25 years 10 years Duration of product presence on the Russian market 9 years 7 years 13 years 10 years More than 16,000 About 10,000 More than 25,000 - More than 50 About 10 More than 100 About 50,002 Availability of implementations at leading enterprises of the Russian defense industry + - - No data Availability of a partner network + + 12 -24 months. 24 -36 months 36 -48 months 9 -24 months Compliance with ISO 9000 standards Total number of implementations in the world Number of implementations in Russia Average duration Slide No. 17
 Results of the analysis of ERP systems for the defense industry: SAP R/3. Leader in the market of automated enterprise management systems. However, these solutions are used only to manage financial and accounting tasks at the level of management companies of large corporations. Experience in manufacturing companies is not so great. SAP R/3 has a high cost of ownership. The source codes of the system have not been transferred to Russian partners. The State Technical Commission has certified only the means of delimiting access rights to the system. Oracle e. Business Suite. Traditionally, Oracle application solutions (except DBMS) are used exclusively to manage the financial activities of companies. As with SAP, the company has virtually no industry experience. Localization and support of the system is carried out by the Company's representative office. The source codes of the system have not been transferred to Russian partners. Baan. A product of SSA Global Corporation, a leader among software manufacturers (up to 40% control) for industrial enterprises. Baan's solutions are considered the best in the world for defense industry enterprises. The source codes of the system are owned by the Russian company Alpha. Integrator”, which refines the system taking into account the requirements of national legislation and ensures the correct transition of users to new versions of the system. Galaktika Corporation continues to try to create production management modules in its system. When developing the system, existing business processes at Russian enterprises were used without their optimization. The proposed model of production management reflects the approaches of the times of centralized planning, and the implementation of such solutions leads to a lag of Russian enterprises in the field of business management. Slide number 18
Results of the analysis of ERP systems for the defense industry: SAP R/3. Leader in the market of automated enterprise management systems. However, these solutions are used only to manage financial and accounting tasks at the level of management companies of large corporations. Experience in manufacturing companies is not so great. SAP R/3 has a high cost of ownership. The source codes of the system have not been transferred to Russian partners. The State Technical Commission has certified only the means of delimiting access rights to the system. Oracle e. Business Suite. Traditionally, Oracle application solutions (except DBMS) are used exclusively to manage the financial activities of companies. As with SAP, the company has virtually no industry experience. Localization and support of the system is carried out by the Company's representative office. The source codes of the system have not been transferred to Russian partners. Baan. A product of SSA Global Corporation, a leader among software manufacturers (up to 40% control) for industrial enterprises. Baan's solutions are considered the best in the world for defense industry enterprises. The source codes of the system are owned by the Russian company Alpha. Integrator”, which refines the system taking into account the requirements of national legislation and ensures the correct transition of users to new versions of the system. Galaktika Corporation continues to try to create production management modules in its system. When developing the system, existing business processes at Russian enterprises were used without their optimization. The proposed model of production management reflects the approaches of the times of centralized planning, and the implementation of such solutions leads to a lag of Russian enterprises in the field of business management. Slide number 18
 Results of the examination: the need to focus on the use of powerful integrated adaptive basic ERP systems; adoption by Russian companies of the most advanced approaches to solving resource management problems proposed by world leaders in ERP solutions; the effectiveness of significantly lower costs on information technology (compared to capital investments in the technical re-equipment of enterprises) with a comparable impact on the growth of labor productivity. Based on the above, we consider it necessary and appropriate to recommend the Russian version of the Baan ERP system, owned by the Alfa Integrator company, as a base system for Russian defense industry enterprises. Slide number 19
Results of the examination: the need to focus on the use of powerful integrated adaptive basic ERP systems; adoption by Russian companies of the most advanced approaches to solving resource management problems proposed by world leaders in ERP solutions; the effectiveness of significantly lower costs on information technology (compared to capital investments in the technical re-equipment of enterprises) with a comparable impact on the growth of labor productivity. Based on the above, we consider it necessary and appropriate to recommend the Russian version of the Baan ERP system, owned by the Alfa Integrator company, as a base system for Russian defense industry enterprises. Slide number 19
 Proposals on the structure of the examination system Ministry of Education and Science Ministry of Industry and Energy Department of International Relations and Information Technologies Department of the Defense Industrial Complex Federal Agency of Industry Interdepartmental Council Federal Agency for Science and Innovation State Research Institute of IT "Informika" Interdepartmental Center for the Development of IPI Technologies Approval Independent experts Examination result ERP developer companies and equipment suppliers Enterprises Universities Slide No. 20
Proposals on the structure of the examination system Ministry of Education and Science Ministry of Industry and Energy Department of International Relations and Information Technologies Department of the Defense Industrial Complex Federal Agency of Industry Interdepartmental Council Federal Agency for Science and Innovation State Research Institute of IT "Informika" Interdepartmental Center for the Development of IPI Technologies Approval Independent experts Examination result ERP developer companies and equipment suppliers Enterprises Universities Slide No. 20
 Order of the Ministry of Industry and Science of Russia No. 277 dated December 23, 2003 “On the creation of an interdepartmental center for the development of IPI technologies” In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Industry and Science of Russia dated November 28, 2003 No. 264 “On the organization of work on the implementation of a comprehensive interdepartmental program for improving the quality of products of the defense industry complex "and to coordinate the implementation of the research work and pilot projects in the field of FPI technologies provided for in the specified program, I ORDER: 1. To assign the functions of an interdepartmental center for the development of FPI technologies to the state institution “State Institute of Information Technologies and Telecommunications” (A. N. Tikhonov) (hereinafter referred to as the Center), entrusting it with organizing and coordinating the implementation of the following set of works at defense industry enterprises: scientific research in the field of IPI technologies; creation and system integration of a set of domestic software products in the field of IPI technologies, ensuring their effective implementation at enterprises in various industries; analysis and examination of foreign software products in order to ensure the safety of their implementation at industrial enterprises; ensuring the implementation of pilot projects for the introduction of IPI technologies carried out within the framework of agreements with the Russian Ministry of Education and Russian agencies for defense industries; creating and ensuring the effective functioning of a system for retraining and advanced training of specialists in the field of IPI technologies using promising educational processes, including distance learning; organizing regional centers for the development of FPI technologies; provision of consulting services in the areas of activity of the Center. 2. ... Acting Minister A. Fursenko Slide No. 21
Order of the Ministry of Industry and Science of Russia No. 277 dated December 23, 2003 “On the creation of an interdepartmental center for the development of IPI technologies” In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Industry and Science of Russia dated November 28, 2003 No. 264 “On the organization of work on the implementation of a comprehensive interdepartmental program for improving the quality of products of the defense industry complex "and to coordinate the implementation of the research work and pilot projects in the field of FPI technologies provided for in the specified program, I ORDER: 1. To assign the functions of an interdepartmental center for the development of FPI technologies to the state institution “State Institute of Information Technologies and Telecommunications” (A. N. Tikhonov) (hereinafter referred to as the Center), entrusting it with organizing and coordinating the implementation of the following set of works at defense industry enterprises: scientific research in the field of IPI technologies; creation and system integration of a set of domestic software products in the field of IPI technologies, ensuring their effective implementation at enterprises in various industries; analysis and examination of foreign software products in order to ensure the safety of their implementation at industrial enterprises; ensuring the implementation of pilot projects for the introduction of IPI technologies carried out within the framework of agreements with the Russian Ministry of Education and Russian agencies for defense industries; creating and ensuring the effective functioning of a system for retraining and advanced training of specialists in the field of IPI technologies using promising educational processes, including distance learning; organizing regional centers for the development of FPI technologies; provision of consulting services in the areas of activity of the Center. 2. ... Acting Minister A. Fursenko Slide No. 21

Implementation of an ERP system at a machine-building enterprise: goals, strategy, experience
Like Share Report 469 Views
Implementation of an ERP system at a machine-building enterprise: goals, strategy, experience. PromIT '13 Minsk May 21, 2013. Contents. 1. About EPAM Systems. 2. Goals of the ERP system implementation project. 3. Strategy for implementing an ERP system. 4 . Experience in implementing SAP ERP implementation projects.
Download Presentation
Implementation of an ERP system at a machine-building enterprise: goals, strategy, experience
E N D - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
No related presentations.
Presentation Transcript
Enterprises Impact of the ERP system Impact Indicators Produce what the market needs Meet and reduce order deadlines Produce quality products Provide quality service Release new products on time Revenue Optimize finished goods inventories Optimize work in progress Optimize material inventories Shorten the production cycle (reduce production delays) Working capital needs means Optimize purchasing costs Optimize production costs Reduce inventory storage costs Costs
High-quality planning Principles of planning Objectives Maintain and reduce order deadlines The production schedule of the GP must correspond to the shipment schedule, reduce the intervals between deliveries (split large deliveries into several smaller ones). The production schedule for batches of DSU must correspond to the production schedule of GP (prevent premature production of DSU), and be produced in smaller batches. The schedule for the release of materials into production must correspond to the schedule for the production of DSE (avoid premature release of materials), release them in smaller batches. The schedule for purchasing materials must correspond to the schedule for releasing them into production (avoid premature purchases), and purchase in smaller batches. Optimize finished product inventories Optimize WIP volumes Optimize material inventories Shorten the production cycle (reduce production delays) Optimize purchasing costs Optimize production costs Reduce inventory storage costs
Flow Sales Supply Production GP Warehouses MTO Warehouses Suppliers Buyers Mechanical processing production Assembly production Procurement production Fulfill the shipment schedule with minimal GP stocks. Carry out the production schedule of GP (evenly) with minimal volumes of work in progress and materials inventories. Do not allow the formation of premature reserves - do not divert resources, do not work to create “blood clots”.
High-quality planning Enterprise management using an ERP system - Effective management based on resource planning By linking the planning of sales, production, purchasing and financial flows, you can increase production volume with the same or even less volume of working capital. High-quality operational scheduling of production tasks, capacities and logistics will allow you to reduce the lead time for fulfilling customer orders, while simultaneously reducing warehouse stocks and work in progress, and ultimately reduce costs in production, procurement, and warehouses. Result Increased profit Increased market value of the enterprise
1. About EPAM Systems 2. Goals of the ERP system implementation project 3. ERP system implementation strategy 4. Experience in implementing SAP ERP implementation projects 5. RDS-EPAM solution
The management of the enterprise wants to increase the viability of the business and understands that it is necessary to improve business processes. Business processes change based on progressive methodologies and the potential of IT systems that implement these methodologies. Option 1 Option 2 The company has a strategy for increasing efficiency. A new methodology for planning and production management is being developed, business processes are being reengineered with maximum use of the best global practices. Automation is performed on the basis of the standard functionality of the ERP system that implements these practices. The company does not have a clear strategy for increasing efficiency. The existing methodology for planning and production management, and the current organization of business processes are automated. The standard functionality of the ERP system changes significantly and/or non-standard functionality is developed. Successful completion Business project IT project Return on investment
Business reorganizations as part of ERP implementation Design Development Implementation Operation Corporate strategy Functional strategy IT strategy Analysis of current business efficiency Business consulting Assessment of economic efficiency from implementation Target model of business processes Organizational structure System of performance indicators Functioning of the Competence Center Formation of the Central Committee Conceptual design of the IT system Development Research and development information Prototype creation IT consulting Prototype integration Solution development Testing and stabilization Replication Integration and other IT initiatives Carrying out changes in business processes, organizational structure and user training Program management Risk management and quality control Program management center
Example: Functional area - Production management and logistics Prerequisites The enterprise strategy contains the task of developing production management. A production top manager has been appointed as the head of the program for the development of production management. Activities Determine performance indicators whose values are not satisfactory to the company's management. Determine target values for these indicators. Identify negative situations in current production and supply planning and management processes that need to be addressed. Develop a target methodology for planning and managing production and supply, based on “best world practices” (international experience). Develop a set of performance indicators for the new methodology. Develop an IT system development strategy to provide information support for the target methodology for production planning and management. Approve the decision of the board of directors to switch to a new methodology. Train managers and specialists on the new methodology. Develop target business process models. Develop and approve a plan for the transition to new business process models, including the implementation of appropriate SAP ERP functionality for these business processes.
ERP systems Master data Registration of purchase agreements Registration of sales agreements Production and supply planning Sales orders Purchase orders Warehouse stocks State production plan Production orders Deployment by workshops/factories? Transfer requisitions Purchase requisitions Planned production orders
Solutions Service maintenance Manufacturing KTP Supply Sales Continuous production Discrete production Production to warehouse Assembly to order Production to order Single custom production Project production…
1. About EPAM Systems 2. Goals of the ERP system implementation project 3. ERP system implementation strategy 4. Experience in implementing SAP ERP implementation projects 5. RDS-EPAM solution
Organizational scale Controlling area - 1 Company codes - 24 Plants - 27 Warehouses >500 Shops involved in main production (MRP areas) >50
Costs Settlements with suppliers Settlements with buyers Financial assets Income Expenses Results Supporting processes: Quality management Personnel management Maintenance management Project management SAP implementation on Gomselmash software Functional scale Included in the project scale ENTERPRISE Project development Strategic planning and analysis of enterprise activities Technical preparation of production Long-term ( for the year) planning of production, purchases and costs Purchasing (execution and accounting) Sales (execution and accounting) Inventories of materials. GP inventories Operational planning of production and supply Supplies of materials (raw materials, services) Supplies of products (products, services) SUPPLIERS Production (execution and accounting) CONSUMERS WIP semi-finished products
Calculation of costs for a product Sales - Production - Costs - Results Start of the planning procedure Analysis of planned expenses and income Planning results Sales planning Planned cost of production and sales Product sales plan Manufacturing option Technical map Specification Production planning Production plan Planned volume of work Planned volume of purchases Planned tariffs of work Cost planning (cost centers, types of work)
1. About EPAM Systems 2. Goals of the ERP system implementation project 3. ERP system implementation strategy 4. Experience in implementing SAP ERP implementation projects 5. RDS-EPAM solution
Problems of manufacturing enterprises Advantages of SAP RDS for business Effective use of standard business processes pre-configured for a manufacturing enterprise Ensuring transparency and efficiency of business processes Unification of business processes Management and control of production processes Conducting business in a single flexible corporate information system Rapid adaptation of users and increasing their productivity work, minimizing costs for personnel training Reducing overall investment risks associated with the RDS project - Rapid Deployment Solutions - Rapid Deployment Solutions
RDS solution Quick results, thanks to standard business processes with pre-configured system functionality containing everything that is needed to manage a manufacturing enterprise SAP authority Stable technology Powerful solution Seamless integration Developed support system Fast and cost-effective Well-defined scope Pre-configured business processes and documents for knowledge transfer Predefined implementation methodology with tools and accelerators Launch into commercial operation within up to 19 weeks Cost-effective Affordable pricing model Attractive services at fixed prices Reduced implementation time, costs and risks Reduced resource requirements for business and IT departments
SAP combines software and services into a new offering that gives you the business functionality you need quickly and affordably SAP Software RDS Implementation Software: SAP Solution Manager 7.0 EHP1 SPS03 RDS Operations Software: SAP ERP 6.0 EHP5 SPS04 SAP Standard Methodology for RDS Implementation Pre-configured business processes SAP Best Practices Package of documents, instructions, accelerators
LLC "Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant - URALTRAK"- a machine-building enterprise for the development and production of wheeled and tracked road construction equipment (bulldozers, pipe layers, front-end loaders, mini tractors), internal combustion engines, spare parts and other high-tech engineering products. The company is part of the structure of OJSC Research and Production Corporation Uralvagonzavod. He is a member of the Association of Defense Industry Enterprises of the Chelyabinsk Region.
Automation goals
The key task that the plant needed to solve at the time of the start of work was the creation of a unified business management system. Therefore, it was decided to automate and standardize all processes and regulatory reference information of the enterprise, introducing a single comprehensive management system "Galaktika ERP" .
The project was implemented by the Ural regional branch of the Galaktika corporation.
Solution
Collaboration with the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant began in 2012. Pre-project work included determining the goals of the work, a detailed examination of the enterprise’s business processes, studying the features of its work, and fixing key tasks. The implementation of the Galaktika ERP system itself began in 2014.
The functions of accounting for the acquisition of inventory, works and services were automated, as well as accounting for the receipt of inventory items from suppliers, material accounting in terms of the movement of inventory items in warehouses and in a number of workshops of auxiliary production, accounting for settlements with accountable persons, currency settlements and calculation of exchange rate differences. A special feature of the project was the painless integration of business processes of a large industrial enterprise into an ERP system, including the use of proprietary software. For example, the integration of operations for the movement of inventory items through warehouses for workshops and specifications of contracts with suppliers, which are recorded in the existing software, has been implemented.
A partner of the Galaktika Corporation, the Business Service company, took part in working with the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant - URALTRAK.
Result
The use of the Galaktika ERP system allowed the company to reduce data processing time. This has a positive effect on the speed and correctness of management decisions, which increases the efficiency of the plant as a whole. In total, during the first stage of the project, about 10 areas of accounting were automated, the number of users at the time of completion of the work was about 120.
Initial problem and tasks
The company used a system developed in Clipper (for entering production data), “1C: Accounting 7.7” (for maintaining regulated accounting) and “1C.8 ZUP” (for payroll calculation). Management was considering the transition to a comprehensive application solution “1C: Manufacturing Enterprise Management 8” (or “1C: ERP 2.0”).
Proposed solution
According to the Customer’s requirements, 2 implementation options were proposed:
1) Automation based on software products “1C: UPP 8” + “PiterSoft: Process Management”
2) Automation based on software products “1C: ERP 2.0”.
Comparative characteristics of the solutions are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Comparative characteristics of the correlation between the Customer’s goals and the functional capabilities of 1C software products
The customer decided to automate using 1C: ERP 2.0.
Result
1. Accounting for production of products produced according to individual orders of customers with their own technical equipment. documentation
2. Monitoring the fulfillment of the buyer’s specifications at all stages (production - quantity, sale - quantity, price), including deadlines
3. Automatic generation of production task
The “Treasury” (planning of income and expenses) and “BDDS” (plan-factual analysis of enterprise cash flows) blocks were launched. The “BDR” block (plan-fact analysis of enterprise income and expenses) was partially launched (the project was suspended due to lack of funding from the Customer)
1. Regulated (both accounting and tax accounting in the system) has been launched.
2. Implemented serial (batch) accounting of materials and finished products
3. Organized the receipt of production costs by order
4. Set up to receive the necessary regulated Accounting and Tax reporting (including consolidated)
1. Automated accounting of customer specifications, calculation of planned cost estimates according to specifications
2. Implemented control over the fulfillment of the buyer’s specifications at all stages (production - quantity, sale - quantity, price), including deadlines
3. Mutual settlements with customers in the context of specification/specification line.
4. A mechanism for automatically generating documents and calculating prices between our own legal entities has been set up.
During the project implementation, the following areas of production activities were automated.